
SEO is an evolving discipline. It’s constantly in a state of flux.
Case in point: Google has already rolled out four major algorithm updates in 2023 so far.
To stay ahead of the game and outrank your competitors in search results, you need to follow the SEO best practices and also follow the current trend to ensure your rankings don’t drop.
Here are the 15 most common SEO mistakes in 2023 and the actionable steps you can take to fix them.
Table of Contents
- 15 Common SEO Mistakes
- Mistake #1: Not Aligning Your Content with Search Intent
- Mistake #2: Not Setting SEO Goals
- Mistake #3: Underestimating Internal Links
- Mistake #4: Not Using a Caching Plugin
- Mistake #5: Ignoring Local SEO
- Mistake #6: Not Having a Mobile Optimized Website
- Mistake #7: Not Optimizing Your XML Sitemap
- Mistake #8: Not Creating Evergreen Content
- Mistake #9: Not Updating Your Content
- Mistake #10: Not Doing Enough Keyword Research
- Mistake #11: Not Converting Brand Mentions into Backlinks
- Mistake #12: Underestimating Title Tags and Meta Descriptions
- Mistake #13: Using Too Many Popups and Email Capture Forms
- Mistake #14: Ignoring Data and Insights from Analytics
- Mistake #15: Neglecting E-A-T
- Final Thoughts
15 Common SEO Mistakes
Mistake #1: Not Aligning Your Content with Search Intent
If you want to rank your pages on Google, you need to create content that aligns with search intent (aka user intent).
In fact, user intent is so important that the phrase is mentioned 333 times in Google’s Quality Raters Guidelines (QRG).
All the top-ranking pages pass Google’s litmus test of creating the exact type of content that searchers are looking for.
So, as a content creator, the most critical SEO mistake you can make is to create content that doesn’t satisfy search intent.
Understanding the search intent of a query is the secret sauce that helps content creators rank their pages on top of Google SERPs.
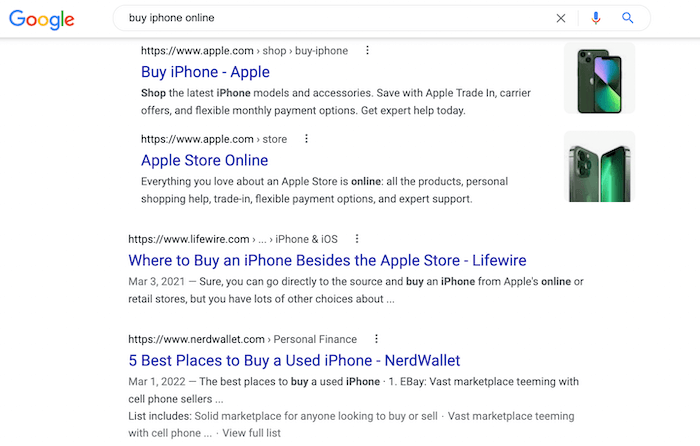
For example, a user who searches for “buy iPhone 15 online” on Google is looking for sites where they can order iPhone 15 online. The intent here is to buy, not to learn about the features of iPhone 15.
Google understands the intent here. Hence the SERPs for this query are filled with eCommerce pages where people can buy the latest iPhone or listicles of websites where people can order the latest iPhone online.
A mistake that many content creators make is targeting the wrong keywords. And in most cases, these keywords are wrong because the interpretation of search intent for these keywords is wrong.
Which is why inferring the search intent of your target keywords is one of the primary things you should be doing before you start creating content.
Typically, there are four types of search intent:
- Informational – when a user is seeking information on a specific topic.
- Commercial – when a user is interested in buying a product or service but hasn’t quite made up their mind yet.
- Transactional – when a user is looking to buy something.
- Navigational – when a searcher is looking for a specific website or webpage.
Here are some examples for each type of search intent:

Semrush is one of the few keyword research tools that shows the search intent of the keywords you’re targeting. So, make sure you pay attention to this information when you’re researching keywords on Semrush.
(Side note: If you aren’t using
Here’s how you can check search intent for keywords on Semrush:
- Enter your target keywords in the search bar
- In the resulting overview report, check the “Intent” section
- Click on “View all” under the Keyword Variations section and pay attention to the Intent column for all the keywords you’d like to use in your content.
To learn more about search intent and how to optimize your content for search intent, check out Search Intent and SEO: The Ultimate Guide.
Mistake #2: Not Setting SEO Goals
When it comes to SEO, setting the right SEO goals is super important. Since SEO’s ROI is in the long run, content creators and SEO professionals often make the mistake of ignoring SEO goals.
Here’s the harsh truth: Without setting SEO goals, you’re unlikely to achieve concrete results.
By setting the right SEO goals, you can bring more clarity and focus to your SEO strategy.
To that end, Ahrefs recommends setting a pyramid-based SEO goal structure.
Here’s what the SEO goal pyramid looks like:
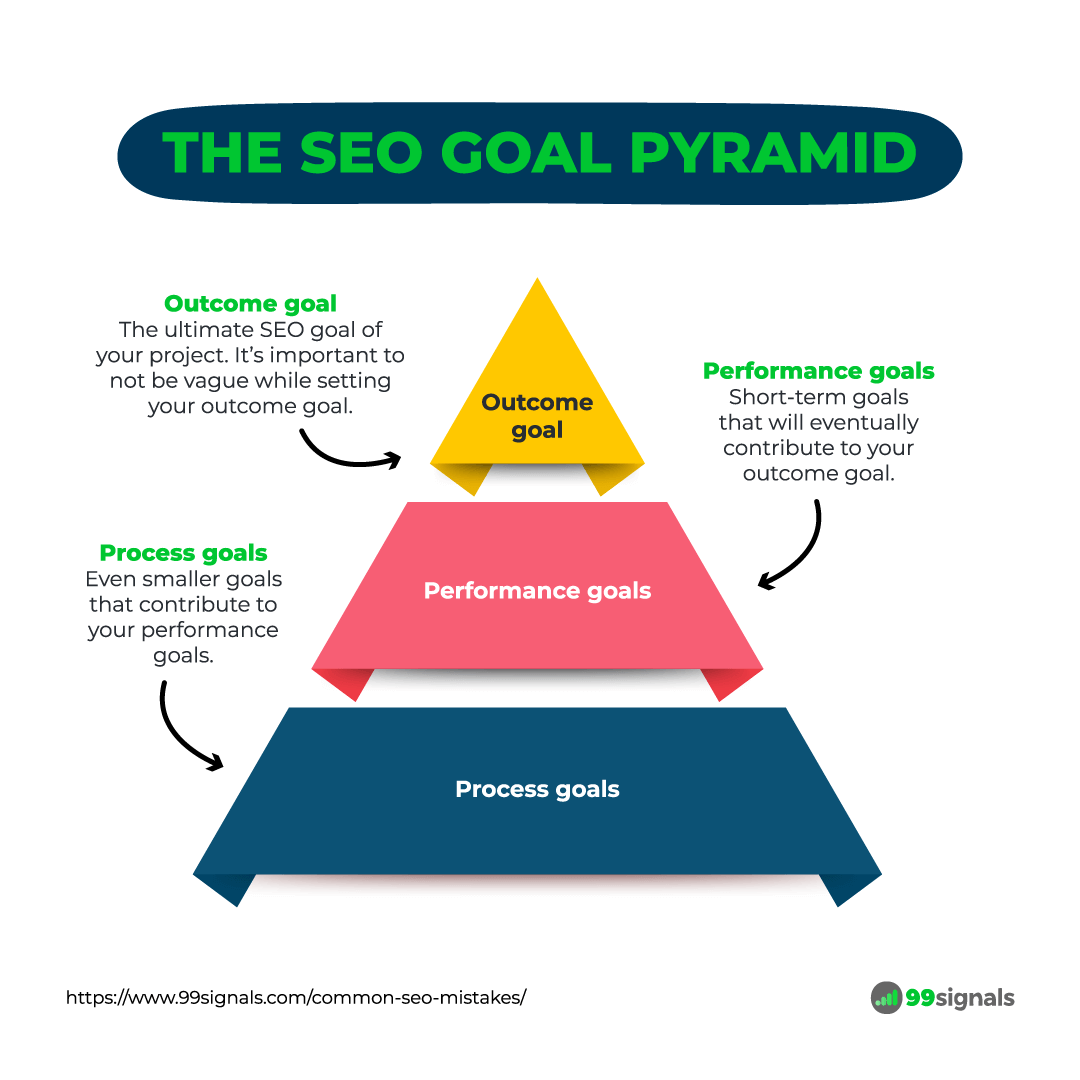
And here’s how you can use it:
- Set an outcome goal: This is the ultimate SEO goal of your project. Visualize what you want to achieve and the time frame you want to achieve it in. It’s important to not be vague while setting your outcome goal. Be specific. An example of a good outcome goal would be “to rank in the top 3 on Google for [your target keywords] in 6 months.”
- Break your outcome goal down into performance goals: These are short-term goals that will eventually contribute to your outcome goal. So, if your outcome goal is “to rank in the top 3 on Google for [your target keywords] in 6 months,” then a good performance goal would be “to generate 25 authoritative backlinks within 6 months.”
- Break your performance goals into process goals: These are even smaller goals that contribute to your performance goals. Continuing with our example of “to rank in the top 3 on Google for [your target keywords] in 6 months,” if the performance goal is “to generate 25 authoritative backlinks within 6 months,” then our process goal can be to “send out 300 outreach emails in 6 months” or if you’re building backlinks through infographics, then your process goal should be to design a high-quality infographic that can submitted to infographic submission sites.
Use a spreadsheet to clearly define your goals and to keep track of your progress.
To learn more about setting the right SEO goals, refer to this post on SEO goals by Ahrefs.
Mistake #3: Underestimating Internal Links
Internal links are links from one page that point to other pages on the same website. From an SEO perspective, internal links are one of the ways Google discovers new content on a website.
According to Databox, a blog post should have 2-5 internal links.
That number seems about right, but it’s important not to go overboard with internal linking. Make sure the internal links are relevant and provide better context for your posts.
Internal linking is not the most interesting aspect of SEO. Which is why it’s often underestimated. But ignoring the internal link structure of your website is one of the biggest SEO mistakes to avoid in 2022.
Luckily, optimizing your internal link structure is one of the easiest SEO hacks you can do to improve your site’s SEO.
Here are some internal linking best practices you should follow:
Link from top-ranking pages
A quick and easy way to transfer link value to a newly-published post is to link to it from a top-performing post on your site.
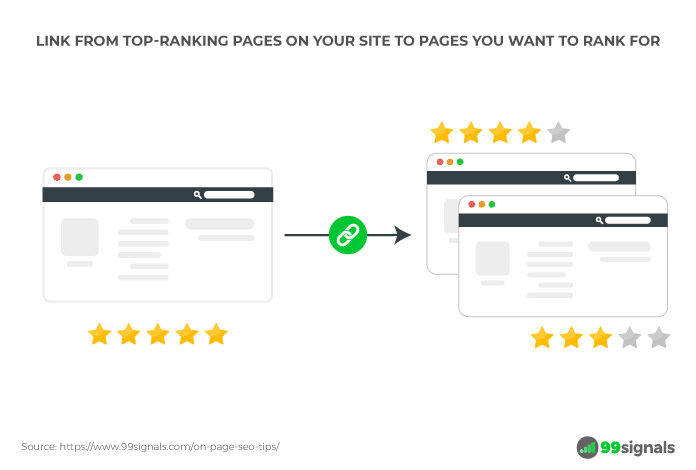
Use a tool like Semrush’s Backlinks Analytics tool to identify a list of the most linked-to pages on your site. Add a link in one of these posts to your recently-published article. But make sure the post is relevant to the topic.
Use keyword-rich anchor text
The more descriptive your anchor text, the easier it is for Google to understand the page you’re linking to and for users to navigate your site. Avoid using generic anchor text like “click here” and “check this out.”
Add internal links to orphan pages
Orphan pages are pages with no internal links. If orphan pages are not listed in your sitemap, they won’t show up in search results. Use Semrush’s Site Audit tool to identify orphan pages on your site.
Make sure none of the important pages on your site are orphan pages.
This is why your recently-published post should always get some internal link juice from one of your top-ranking posts.
Perform a basic internal link audit with Google Search Console
With Google Search Console, you can examine how your internal links are set up. You can also identify unimportant pages that have too many internal links pointing to them. Reduce the number of internal links to these pages and point them to important pages on your site.
Recommended reading: Internal Links for SEO: The Definitive Guide
Mistake #4: Not Using a Caching Plugin
Site speed is a critical factor that influences your site’s rankings. A site that loads faster also contributes to a superior user experience. After all, you wouldn’t want visitors on your site waiting around for pages to load.
According to Backlinko, pages on sites that load quickly rank significantly higher than pages on sites that load slowly.
One way you can speed up your website is to install a caching plugin. With a caching plugin, you can significantly reduce your load time and improve your Google PageSpeed and Core Web Vitals scores.
If you use WordPress, there’s a variety of free and paid caching plugins available on the market.
The three most popular free caching plugins on WordPress are:
- W3 Total Cache
- WP Fastest Cache
- WP-Optimize
But if I were to offer my personal recommendation, it’d have to be WP Rocket. It costs $49/year, but makes a huge difference to your site speed.
So, if you can afford it, go for WP Rocket. If you’re just starting out, then go with any of the free caching plugins listed above.
Related: 19 Best SEO Plugins for WordPress
Mistake #5: Ignoring Local SEO
46% of all Google searches are local.
If your business operates out of a single location or if most of your customers are from just one location, then optimizing for local search is a must.
Yet there are several businesses that haven’t even claimed their Google My Business (GMB) listing.
Claiming and optimizing your Google My Business listing should be the starting step in optimizing your website for local search results.
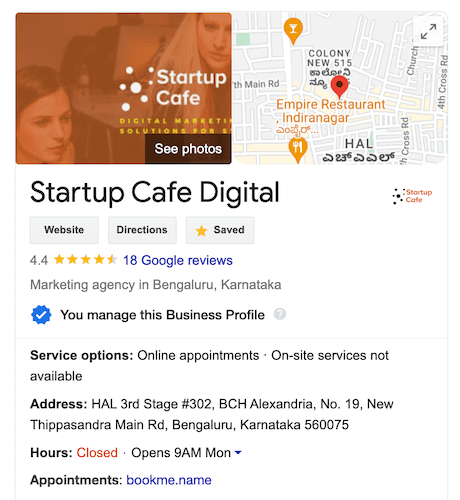
Once you’ve done that, you can claim and optimize your Bing Places and Apple Maps listings.
Next, you can follow these local SEO best practices:
- Create a ‘contact’ and ‘about’ page on your website.
- On the contact page, include the complete name of your business, address, phone number (NAP), and email address.
- Ensure that your phone number is clickable via mobile.
- Ensure that your contact details are consistent on all pages where they are mentioned.
- Mention your office address and email address in the website’s footer.
- Add a Google Map to your contact page to make it easier for prospects to find you.
- Make your website 100% mobile-friendly.
- If you operate from multiple locations, each location should have its own dedicated page.
- Perform weekly site audits using a tool like Semrush to fix the most common types of error in SEO.
To help with the above recommendations, you can check out any of these local SEO tools to optimize your website for local search.
Mistake #6: Not Having a Mobile Optimized Website
This may seem like an obvious point, but you’d be surprised to learn how many mainstream sites are not optimized for mobile.
Case in point: Here’s the mobile performance of The Washington Post:
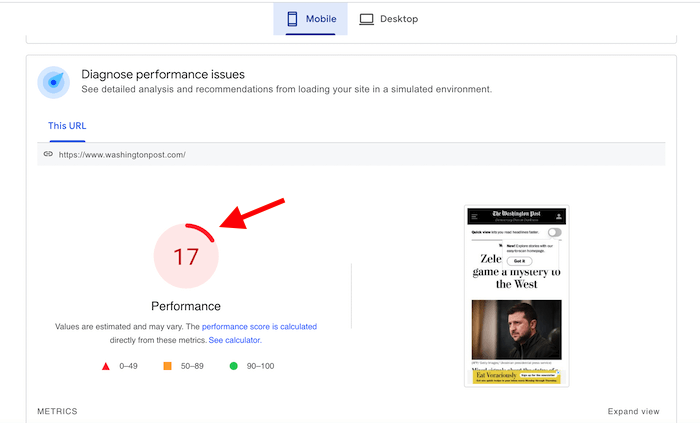
You can have the best content in the world, but if your website is not mobile-friendly, you’re going to miss out on a large chunk of your target audience.

The importance of having a mobile-friendly website has only grown in recent years. Since Google’s “mobilegeddon” algorithm update, optimizing websites for mobile has become a priority for SEOs.
In 2019, Google announced mobile-first indexing, which means Google predominantly uses the mobile version of the content for indexing and ranking.
So in order to stay relevant and beat your competitors in SERPs, you need to ensure your website delivers a fast and mobile-friendly user experience.
Here are some steps you can take to make sure your site is mobile-friendly:
- Follow mobile design best practices: You can get this info from Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test or from your Google Search Console account.
- Run site audits twice a month to identify and fix mobile issues.
- Ensure your website follows responsive design.
- Make sure you deactivate interstitial popups on mobile.
- Provide easy readability. Use a legible font size and choose a typeface that works well in multiple sizes.
Mistake #7: Not Optimizing Your XML Sitemap
An XML sitemap informs search engines about all the pages that exist on your website. Without a sitemap, Google may find it difficult to crawl and index all the pages on your website.
Which is why it’s important to create and optimize your XML sitemap to ensure Google discovers pages on your site faster.
If you use WordPress, then you can use the Yoast SEO plugin to generate a sitemap for your site.
Side note: Yoast isn’t just useful for generating your sitemap, but it’s the best WordPress SEO plugin you can use to improve your meta tags and fix other critical on-page SEO mistakes.
To generate an XML sitemap through Yoast SEO, navigate to:
SEO > General > Features
Just turn the “XML sitemaps” toggle on to generate your sitemap.

You can view your sitemap at yourwebsite.com/sitemap_index.xml.
Another advantage of using Yoast is that it will automatically ensure all of the noindexed pages remain excluded from indexing.
Once your sitemap is ready, you need to submit it to Google Search Console.
Follow these steps to successfully submit your sitemap to Google:
- Sign in to your Google Search Console account
- Select your property
- One the sidebar menu, select Sitemaps
- Enter your sitemap URL
- Click the “Submit” button
Once your sitemap is submitted, Google will periodically scan your sitemap to find new pages.
Recommended reading: How to Create an XML Sitemap for Your Website (and Submit it to Google)
Mistake #8: Not Creating Evergreen Content
Evergreen content is a collection of articles on your blog that stay relevant for a long period of time. A good example of an evergreen post in the SEO space would be this beginner’s guide to link building by Ahrefs:
Or, take this post on the list of best books for entrepreneurs from our own blog:

Here’s the 3-step process you need to follow to create evergreen content:
- Find keywords with a decent search volume – Use an SEO tool like Semrush or Serpstat to find keywords with a decent search volume. Make sure your target keywords are not news-focused or seasonal keywords.
- Create 10x content – Once you’ve identified the keywords, you need to make your post 10 times better than the highest ranking search result for your target keywords. This type of content is referred to as 10x content. If your post is only slightly better than the top-ranking post, you may not rank on top of SERPs in the long run. But when you publish a blog post that is 10x, like in the case of Ahrefs’ Beginner’s Guide to Link Building, your organic competitors are going to find it difficult to outrank you in SERPs.
- Update and relaunch – An evergreen post typically doesn’t need to be updated as often as regular posts. But it’s an SEO best practice to update it from time to time with fresh insights and information to maintain its relevance. Doing so will protect its organic ranking and the post’s ability to generate links naturally. I keep updating and relaunching my top-performing posts whenever I notice a declining trend in organic traffic. (More on this next)
Mistake #9: Not Updating Your Content
If you want to shield your articles from periodic drops in organic traffic, then you need to update your posts and relaunch them at regular intervals.
It’s a solid SEO strategy that can guarantee higher search rankings. And yet, it’s often overlooked by most bloggers and SEOs because it involves revisiting old posts and updating them with fresh, relevant information.
But updating and relaunching your old posts is one of the most effective tactics to generate even more traffic for posts that are already getting a decent amount of search traffic.
In fact, using this tactic, I was able to boost organic traffic to one of my old posts by 146% and move its organic ranking from position #5 to position #1. You can read more about it in this SEO case study here:
Here’s the 5-step content update process that I follow to generate more traffic for old posts:
1. Identify the post that needs an update
Visit your Google Search Console account to identify posts that have witnessed decline in organic traffic. You can do this by visiting the Search results report and clicking on date and choosing the “Compare last 6 months to previous period” filter. Sort the results by “Clicks difference” from low to high. Pick a post that has seen the highest decline in value.
Alternatively, you can use a free tool like Animalz Revive to identify underperforming blog posts.
This tool analyzes your Google Analytics data and provides a list of posts that need to be refreshed.
2. Update your content with new information
The next step is to update your content with new and fresh information. Check out some of your competitors’ posts on the same topic that are outranking you in SERPs. See what your article is currently missing — add unique insights, provide examples, and address more pain points. Add an FAQs section to your post to have a greater chance of ranking in Google’s featured snippets.
3. Optimize your target keywords
Don’t repeat your target keywords too many times. Instead, use keyword variations like related keywords or question-based keywords. Use a tool like Semrush to identify long-tail keyword variations for your target keywords.
4. Add new visuals
Use images, screenshots, and videos to supplement your content. Make sure your updated content has new and improved visuals to improve user engagement.
5. Relaunch the post
Make sure you change the “published” date of the article to the current date. This updated date will be highlighted in SERPs.
I follow this 5-step process for cornerstone content on my blog once every three months. You can do the same to revive some of your older posts and breathe new life into them.
Recommended reading: Content Upgrade Strategy: How to Optimize Old Blog Posts to Get More Traffic
Mistake #10: Not Doing Enough Keyword Research
Here’s a simple question you need to ask yourself before you start working on a new blog post: Are you writing on a topic that your audience likes or something that you like? If the answer to this question is latter, then you shouldn’t be disappointed when the post doesn’t generate any organic traffic.
I’ve had several clients at my digital agency who were under the impression they had the best ideas for blog posts in their niche. But when I did a bit of research on the topic, I found that the search volume for these keywords was either non-existent or too small to justify a blog post.
You may have the best intentions, but assuming that your audience is ready and eager to read anything you publish is just not a good practice.
One of the biggest SEO mistakes you can make is try to create content without identifying the most popular topics and subtopics through keyword research first. I’ve noticed a lot of startups and small businesses falling prey to this fallacy and it’s amongst the most common SEO mistakes small businesses must avoid.
There’s no easy way to put this: In order to rank higher in search results, you need to master keyword research.
While you can get a ton of valuable insights from free Google tools like Google Trends and Google’s Keyword Planner, you’ll miss out on key insights if you don’t subscribe to premium SEO tools.
To that end, I’d recommend two SEO tools that are perfect for keyword research out of a plethora of premium SEO tools on the market: Semrush and Serpstat.
Semrush is, hands down, the best keyword research tool on the market.
Semrush’s ability to conjure up keywords and offer data on competitor and question-based keywords is second to none. With over 20 billion keywords and 142 geo databases,
Whether you’re looking for quick keyword data or deeper keyword research data like keyword variations and advanced keyword research,
Sign up for a 14-day free trial of
There’s only one drawback: Since
If you’re looking for a budget-friendly SEO tool that’s best for keyword research and not too heavy on the pockets, then you should go for Serpstat. The basic plan of Serpstat is priced at $50/month.
If you’d like a deeper understanding of how to get the best out of both these tools, check out their in-depth reviews below:
Mistake #11: Not Converting Brand Mentions into Backlinks
You can’t expect to rank on top of SERPs for your target keywords without building high-quality backlinks. Especially if there is stiff competition for those keywords.
Link building remains one of the most challenging aspects of SEO. But there is a link building method that is relatively easy: link reclamation.
Link reclamation is the process of converting brand mentions into backlinks. Since it’s so easy to do, it’s also easy to ignore or procrastinate over. And failing to convert brand mentions into backlinks can make you miss out on some of the most authoritative backlinks your site can obtain.
Here’s how it works:
- First, find mentions of your brand that don’t link back to your site. Use a tool like BuzzSumo or Google Alerts to find unlinked mentions of your brand. On Buzzsumo, you can also setup a content alert for your brand or domain, so you get an email whenever someone mentions your brand.
- Next, use a tool like FindThatLead to find and verify the email addresses of the people you want to reach out to.
- Then you send an email to the person with a friendly request to add the link. You can use any of these blogger outreach tools to send bulk outreach emails.
Need an example of how link reclamation works? Below is a link reclamation email I received from Canva:
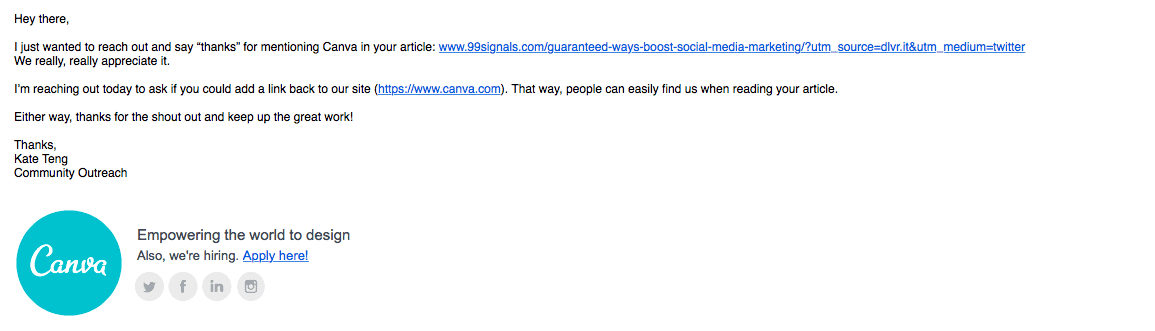
Needless to say, I added a link back to Canva. In most cases, it’s as simple as that.
So don’t miss out on an opportunity to get easy backlinks.
You may be asking yourself: Are title tags and meta descriptions still considered important? The answer is yes.
Title tags remain the second most important on-page ranking factor, after content. On the other hand, while meta descriptions are not a direct ranking signal, they do impact your organic click-through-rate (aka organic CTR).

When it comes to title tags, it’s best to heed Google’s advice:
Titles are critical to giving users a quick insight into the content of a result and why it’s relevant to their query. It’s often the primary piece of information people use to decide which result to click on, so it’s important to use high-quality title text on your web pages.
Here are some title tag best practices to keep in mind:
- Make sure a title tag is present across all your pages
- Keep your title tags brief yet compelling
- Don’t use vague titles
- Use title case or sentence case
- Add your target keywords, but avoid keyword stuffing
- Avoid clickbait headlines.
Pro Tip: Use a free tool like Headline Analyzer to create compelling title tags for your blog posts.
Next, let’s examine meta descriptions.
Here’s what Google says about meta descriptions:
A meta description tag generally informs and interests users with a short, relevant summary of what a particular page is about. They are like a pitch that convince the user that the page is exactly what they’re looking for.
Here are some meta description best practices you should follow:
- Keep it under 160 characters
- Write unique descriptions for each page
- Match search intent
- Ensure your summary best describes the content of your page
- Use sentence case
- Avoid clickbait descriptions.
Since both these meta tags influence organic CTR, it’s important that you spend some time crafting the best possible title tags and meta descriptions for your posts.
Recommended reading: Meta Tags for SEO: The Definitive Guide
Mistake #13: Using Too Many Popups and Email Capture Forms
Think back to the last few websites you visited. In all likelihood, in most cases you were greeted by an annoying popup as soon as you landed on their page. This intrusive practice is all too common on the web.

A lot of marketing blogs are guilty of using intrusive popups to capture email addresses and I confess I’ve been guilty of using them in the past as well.
This is a problematic trend that’s not just restricted to the online marketing industry anymore. Even reputed publications like The New Yorker and The Economist are guilty of this intrusive practice:
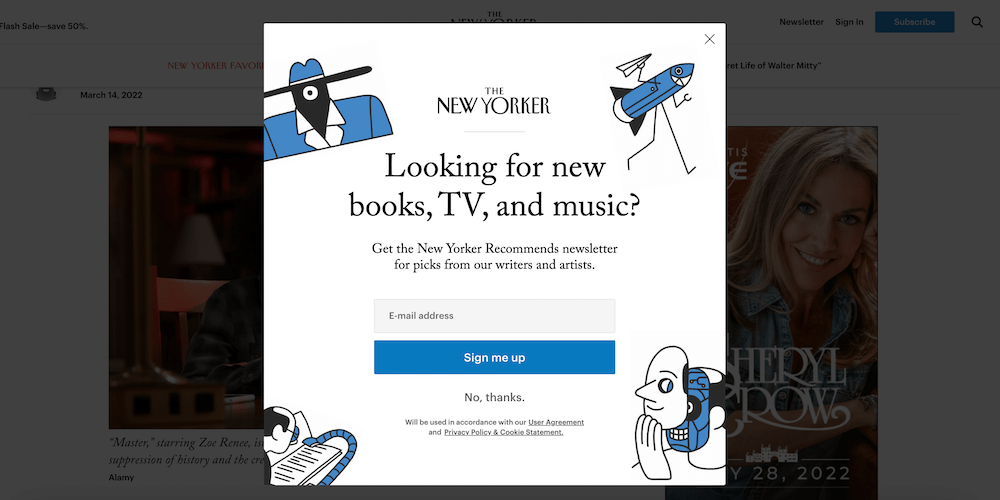
While it’s important to build your email list, it shouldn’t be done at the cost of user experience. Doing so will lead to pogo-sticking (a situation where a user quickly navigates back to the SERPs after landing on your page), which will ultimately derail your rankings.
So what’s the solution?
An easy solution would be to get rid of popups and email capture forms entirely. But that’s not practical advice. As marketers, building an email list is crucial.
Here’s the truth: It’s not the popups themselves that are annoying. It’s the timing of those popups.
For that reason, I’d recommend you use exit-intent popups.
This is how an exit-intent popup works:

GIF Credit: OptinMonster
As you can see above, these popups get activated when a user decides to leave your website. As a result, they are the least intrusive type of popups out there.
This is a controversial opinion, and I know a lot of marketers who would advocate getting rid of popups entirely. But building an email list is one of the most effective ways to promote your content and grow your audience. As such, I’d suggest you use exit-intent popups to build your list.
All the leading email capture tools allow you to enable this option with their popups. Here are some of the best email capture tools you can choose from.
Mistake #14: Ignoring Data and Insights from Analytics
The most effective way to ensure you’re on the right track is to track the progress of your content marketing and SEO efforts.
Once you’ve set your SEO goals (see #2), you need to keep a track of the most important SEO metrics.
To that end, data and insights generated via analytics tools such as Google Analytics and Google Search Console are crucial to staying at the top of your game.
Yet there are some marketers who downplay the importance of analytics and disregard key data in their analytics reports.
Ignoring important SEO metrics can prove detrimental to your site’s rankings.
As such, it’s imperative that you keep a tab on your site’s performance.
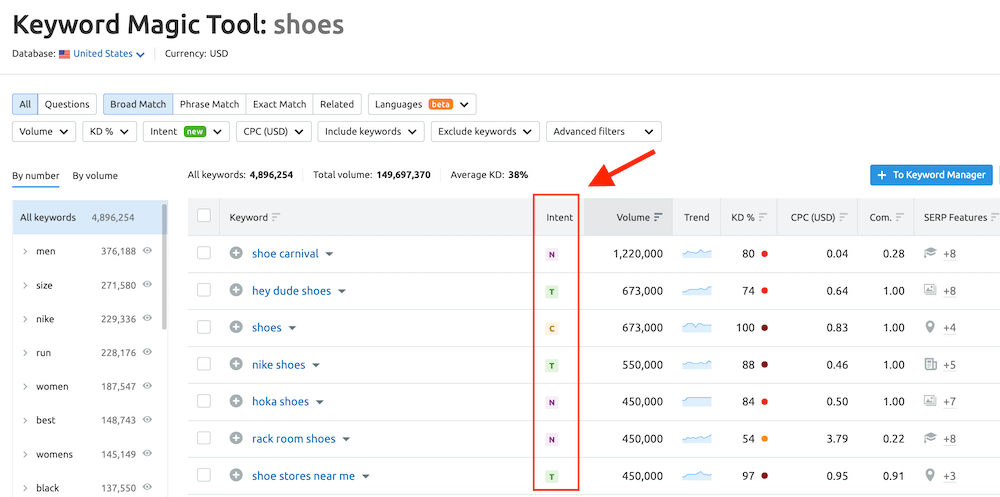
In the context of SEO, here are the 10 most important performance metrics that are worth tracking:
- Organic Traffic – any traffic that comes to your site from a search engine that doesn’t include traffic from paid results. You can track it in Google Analytics.
- Keyword Rankings – these refer to a website’s organic ranking positions for different keywords. Use Semrush or Serpstat to check your keyword rankings.
- Referring Domains – these are websites that link to your website. Use
Semrush to track your referring domains. - Core Web Vitals (CWV) – three important technical SEO metrics that measure your site’s speed and performance. Access the CWV report in your Google Search Console account. You can also use Google’s PageSpeed Insights to check your CWV score.
- Mobile Traffic – you can check your site’s mobile traffic in Google Analytics. Use Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test to test the mobile-friendliness of your website.
- Indexed Pages – these are pages that have been crawled by Googlebot and stored in the Google index. To get an accurate summary of your indexed pages, check the coverage report in your Google Search Console account.
- Traffic Cost – an estimate of how much you’d spend on Google Ads to generate the same traffic you’re currently getting from organic search. Use
Semrush to determine your site’s traffic cost. - Website Health Score – this is the technical SEO score of your website. The higher the score, the less you need to worry about technical SEO. Use Semrush’s Site Audit tool to measure the technical SEO health of your website.
- Average CTR – the percentage of users who click through your site in Google SERPs. Refer to tips outlined in Mistake #12 to improve your organic CTR.
- Bounce Rate – the percentage of visitors who leave your website after visiting just one page. You can check the bounce rate of your pages in Google Analytics.
To learn more about these metrics and the best ways to track them, check out our in-depth post on SEO metrics.
Mistake #15: Neglecting E-A-T
E-A-T stands for Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness. It first became a part of the SEO lexicon when Google released its Search Quality Rater Guidelines (QRG) in 2015.
In the document, Google specifically stated that E-A-T is one of the most important factors that it looks into while evaluating the overall quality of webpages.
In fact, E-A-T is so critical to Google that the term has been mentioned 186 times in the QRG document.
So how do you demonstrate E-A-T with your content? We have already discussed three ways you can do that: pay attention to search intent, content upgrade, and keyword research (refer to tips discussed in mistake #1, #mistake #9, and mistake #10 respectively.)
In addition to these tips, here are some more ways you can demonstrate E-A-T with your content and rank higher on Google:
- Build authoritative backlinks – Despite several algorithm updates and over 200 Google ranking factors, backlinks still remain fundamental to organic search rankings. If you’re not serious about link building, then you’ll have a slim chance of outranking your competitors in SERPs. We have already discussed an easy way to earn backlinks: link reclamation (see mistake #11). Here are some more powerful link building strategies that work.
- Optimize your author bio – A bit of humble bragging in your author bio goes a long way in demonstrating E-A-T. Make sure the “About Me” page of your website has sufficient information about your expertise, experience, and accolades. If you have glowing testimonials from other influential bloggers or top publications in your industry or you’ve won awards that you’re proud of, flex your credentials here.
- Get reviews and customer testimonials – Using reviews is not just good from an E-A-T perspective, but reviews can also influence behavior and reduce customers’ level of anxiety surrounding any purchase they are likely to make on your site.
Recommended reading: Google E-A-T: How to Create Content That Ranks Higher on Google
Final Thoughts
Avoid the aforementioned SEO mistakes like the plague and you should see drastic improvements in your search rankings.
To summarize, here’s a quick recap of all the mistakes in my “SEO: What Not to Do” list:
- Mistake #1: Not Aligning Your Content with Search Intent
- Mistake #2: Not Setting SEO Goals
- Mistake #3: Underestimating Internal Links
- Mistake #4: Not Using a Caching Plugin
- Mistake #5: Ignoring Local SEO
- Mistake #6: Not Having a Mobile Optimized Website
- Mistake #7: Not Optimizing Your XML Sitemap
- Mistake #8: Not Creating Evergreen Content
- Mistake #9: Not Updating Your Content
- Mistake #10: Not Doing Enough Keyword Research
- Mistake #11: Not Converting Brand Mentions into Backlinks
- Mistake #12: Underestimating Title Tags and Meta Descriptions
- Mistake #13: Using Too Many Popups and Email Capture Forms
- Mistake #14: Ignoring Data and Insights from Analytics
- Mistake #15: Neglecting E-A-T (Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness)
Have you been guilty of any of these common SEO mistakes? What other major SEO faux pas do you think should be added to this list? Please share your thoughts in the comments section below.
Editor’s Note: This article was first published on March 19, 2022 and has been updated regularly since then for relevance, freshness, and comprehensiveness.
Related Articles









[…] strategy. However, there are some common mistakes that may make your efforts less impactful. Check out this 99signals post by Sandeep Mallya to learn which errors to […]